Have you ever experienced your computer freezing during an intense gaming session, or watched helplessly as your video rendering progress stalled after hours of work? These frustrating moments might not be caused by insufficient hardware or software issues, but rather by overheating components.
Just as humans suffer heatstroke in scorching weather, electronic devices generate substantial heat during prolonged high-performance operation. Without proper cooling, this heat accumulation leads to performance throttling and potential hardware damage. The unsung hero preventing such thermal disasters is the heat sink - the electronic equivalent of fever-reducing medication for your devices.
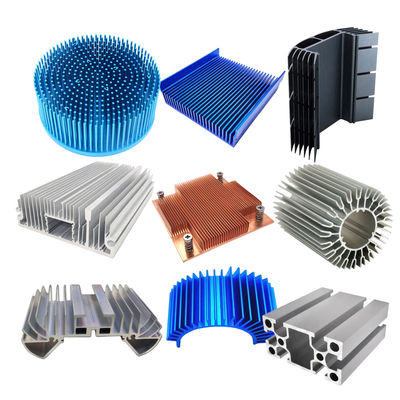
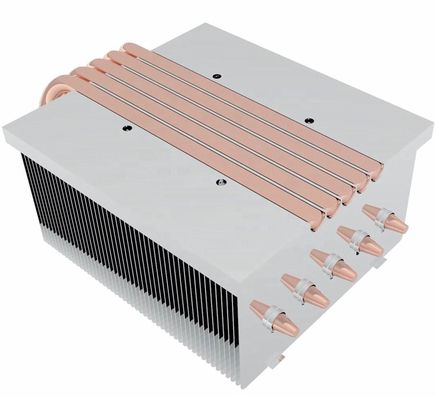
Heat Sinks: The Foundation of Stable Performance
Imagine your CPU as a tireless worker performing complex calculations. Like a high-powered engine, it generates significant heat during operation. Without proper cooling, temperatures rise rapidly, causing performance degradation or even permanent damage. Heat sinks serve as thermal regulators, absorbing and dissipating this heat through two primary mechanisms:
-
Conduction:
Heat transfers from the CPU to the heat sink base, then through the material (typically copper or aluminum) to the fins, much like a relay race passing thermal energy.
-
Convection:
Natural air currents form as heated air rises from the fins' surfaces, creating continuous cooling circulation similar to wind patterns.
Active vs. Passive Cooling: Choosing the Right Approach
Heat sinks fall into two categories based on their cooling methodology:
Active Cooling Systems
These systems employ forced air movement for enhanced cooling:
-
Air Cooling:
Utilizes fans blowing directly across fin arrays, offering straightforward effectiveness like an electric fan.
-
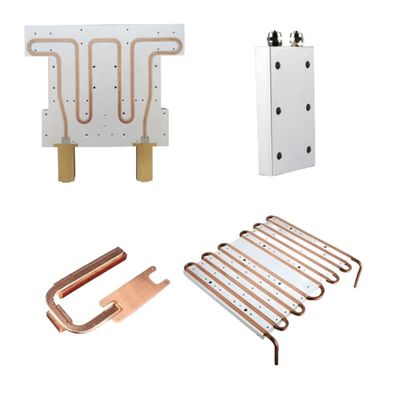
Liquid Cooling:
Employs coolant circulation through a closed loop containing a pump, water block, radiator, and tubing for superior thermal transfer.
While active systems deliver excellent cooling performance, they generate audible noise and require additional power.
Passive Cooling Systems
These rely solely on natural convection, featuring extensive fin arrays to maximize surface area. Their silent operation and reliability suit low-power applications or noise-sensitive environments, though with limited cooling capacity.
Hybrid solutions combine both approaches, using low-speed fans with passive designs for balanced performance and acoustics.
Material Matters: Copper vs. Aluminum
The choice of heat sink material significantly impacts thermal performance:
-
Copper:
Offers superior thermal conductivity (approximately double aluminum's) but comes with higher density, cost, and manufacturing complexity.
-
Aluminum:
Provides adequate conductivity with lighter weight, lower cost, and easier fabrication through extrusion processes.
Premium solutions often combine both materials, using copper bases for optimal heat absorption and aluminum fins for efficient dissipation.
Engineering Excellence: Fin Design Principles
Fin geometry represents a critical design consideration:
-
Parallel Fins:
Standard straight-fin configuration offering straightforward airflow management
-
Pin-Fin Arrays:
Perforated designs enhancing air permeability for high-density applications
-
Soldered Fins:
High-performance bonding ensuring structural integrity and thermal transfer
Optimal designs balance fin density, spacing, and shape to maximize surface area without impeding airflow.
Selection Criteria: Choosing the Right Cooler
Key factors for heat sink selection include:
-
Thermal Design Power (TDP) requirements matching component specifications
-
Physical dimensions compatible with device enclosures
-
Noise tolerance and acoustic preferences
-
Budget constraints and value considerations
Additional recommendations:
-
Verify interface compatibility with motherboard sockets
-
Consider thermal compound quality for optimal contact
-
Evaluate cooling capacity metrics (W or °C/W ratings)
Thermal Innovation: Emerging Technologies
The cooling industry continues to evolve with advanced materials and techniques:
-
Graphene:
Exceptional thermal conductivity from single-layer carbon lattices
-
Carbon Nanotubes:
Nanoscale structures combining thermal and mechanical advantages
-
Enhanced Liquid Cooling:
Improved pump designs and coolant formulations
-
Heat Pipe Technology:
Vapor-chamber systems for efficient heat transport
Thermal Challenges in Modern Computing
Contemporary systems face escalating cooling demands:
-
5G Infrastructure:
High-density processing creates concentrated heat loads requiring advanced thermal management
-
High-Performance Computing:
Server farms and workstations necessitate robust cooling solutions for sustained operation
Proper thermal management not only ensures performance but extends hardware lifespan by preventing thermal degradation.
Maintenance Considerations
-
Regular cleaning to prevent dust accumulation
-
Proper application of thermal interface materials
-
Optimized chassis airflow patterns
-
Continuous temperature monitoring
When servicing cooling systems, exercise caution to avoid component damage, consulting professionals when necessary.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!