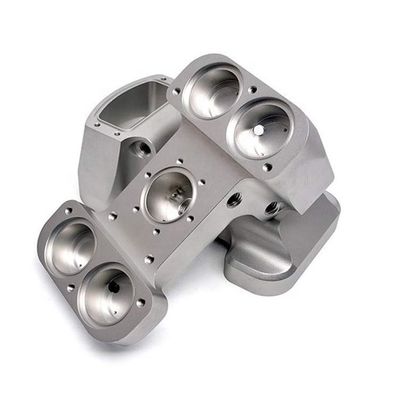
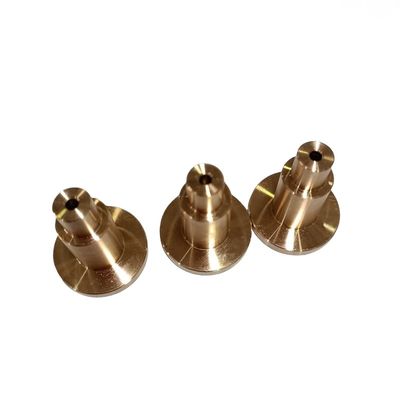
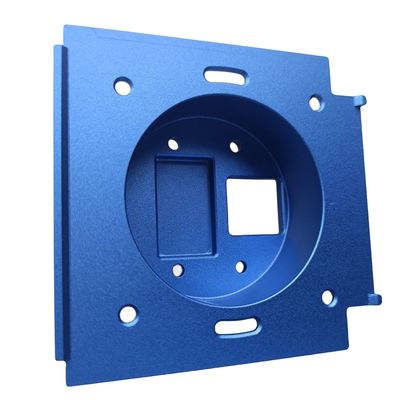
In modern industrial systems, metal casting plays a pivotal role across automotive, aerospace, and electronics sectors. The quality of cast components directly impacts product performance, reliability, and safety. This article examines metal casting through an analytical lens, exploring how data-driven methods can optimize each stage of production.
Part 1: Casting Process Overview - Traditional Meets Modern
1.1 Traditional Casting Methods: Comparative Analysis
Manufacturers choose between several casting techniques based on production requirements:
-
Sand casting: Cost-effective for large components but offers limited precision
-
Die casting: High-volume production with material limitations
-
Investment casting: Superior accuracy for complex geometries
-
3D printing: Customization flexibility with higher costs
1.2 The Investment Casting Advantage
Despite emerging technologies, investment casting maintains distinct benefits for high-volume production:
-
Tolerances reaching IT6-IT8 grade
-
Surface finishes of Ra1.6-Ra3.2μm
-
Capability for intricate internal geometries
-
Broad material compatibility
Part 2: Mold Fabrication - Precision Foundations
2.1 Mold Quality Correlation
Initial mold creation establishes critical quality parameters. Data analysis reveals direct relationships between:
-
Mold dimensional accuracy and final product tolerances
-
Surface roughness and casting finish quality
2.2 Material Selection Matrix
Mold materials present distinct performance characteristics:
-
Wood: Cost-efficient but dimensionally unstable
-
Metal: High stability with greater expense
-
Plastic: Balanced properties with thermal limitations
Part 3: Shell Building - Layered Precision
3.1 Shell Construction Parameters
The investment casting shell process requires 6-8 coating layers, with key quality indicators including:
-
Shell thickness uniformity
-
Structural integrity under thermal stress
-
Gas permeability characteristics
3.2 Slurry Composition Optimization
Refractory slurry formulations balance multiple properties:
-
Thermal resistance thresholds
-
Binding agent effectiveness
-
Additive performance metrics
Part 4: Melting & Pouring - Controlled Transformation
4.1 Metallurgical Process Control
Precise temperature regulation varies significantly by alloy:
-
Aluminum: 700-750°C range
-
Steel: Above 1500°C requirements
4.2 Pouring Method Selection
Different pouring techniques address specific production needs:
-
Gravity pouring: Standard implementation
-
Pressure pouring: Enhanced mold filling
-
Vacuum pouring: Reduced gas porosity
Part 5: Finishing Processes - Quality Validation
5.1 Heat Treatment Variables
Post-casting thermal processing modifies material properties through controlled:
-
Temperature profiles
-
Soaking durations
-
Cooling rates
5.2 Inspection Methodologies
Comprehensive testing protocols evaluate:
-
Dimensional compliance
-
Surface integrity
-
Internal soundness
-
Mechanical performance
The future of metal casting lies in increasingly sophisticated data integration, enabling manufacturers to optimize production variables, reduce costs, and enhance product quality through empirical process refinement.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!